Preventing Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is a significant health concern affecting millions of women worldwide. While certain risk factors, such as genetics and age, are beyond our control, there are proactive steps women can take to reduce their risk and promote breast health. Here are essential guidelines for breast cancer prevention:
Regular Screening:
Regular breast cancer screening, including clinical breast examinations and mammograms as per recommended guidelines, is crucial for early detection. Early detection increases the chances of successful treatment and improves overall outcomes.
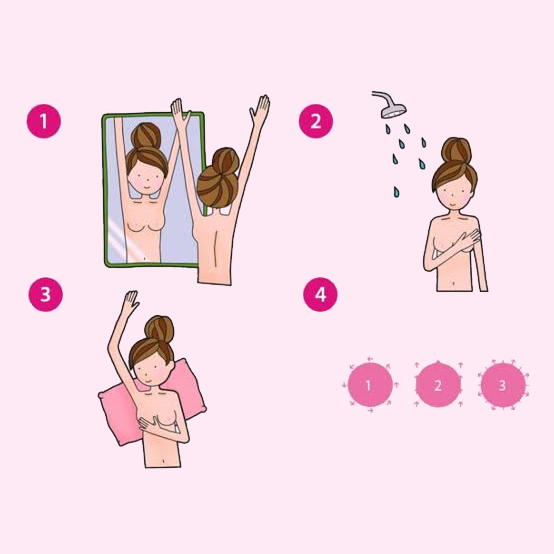
Self Breast Examination (SBE):
Encourage women to perform monthly self-breast examinations to become familiar with their breast tissue and detect any changes promptly. While SBE should not replace clinical exams or mammograms, it enhances the likelihood of detecting abnormalities early on.
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Obesity is linked to an increased risk of breast cancer, especially after menopause. Adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity can help women maintain a healthy weight and reduce their risk.
Stay Physically Active:
Regular physical activity has numerous health benefits, including reducing breast cancer risk. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise weekly.
Limit Alcohol Consumption:
Alcohol consumption is associated with a higher risk of breast cancer. Women should limit alcohol intake, with the American Cancer Society recommending no more than one drink per day.
Avoid Tobacco and passive Smoke:
Smoking is linked to various cancers, including breast cancer. Encourage women to quit smoking and avoid exposure to passive smoking.
Breastfeed, If Possible:
Breastfeeding has shown to have a protective effect against breast cancer. Women are encouraged to breastfeed their babies, as it may contribute to lowering their breast cancer risk.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) Consideration:
If women are considering hormone replacement therapy for menopausal symptoms, they should discuss the potential risks and benefits with their healthcare provider. HRT, particularly combined estrogen-progestin therapy, may increase breast cancer risk.
Limit Exposure to Radiation and Environmental Toxins:
Minimize exposure to unnecessary medical radiation and environmental toxins whenever possible. Be aware of potential carcinogens in personal care products and household cleaners.
Conclusion:
Breast cancer prevention is a multifaceted approach that involves regular screenings, healthy lifestyle choices, and awareness. By taking proactive steps and making informed decisions, women can significantly reduce their risk of breast cancer and lead healthier lives. Encouraging women to prioritize their breast health and empowering them with knowledge is a fundamental aspect of comprehensive healthcare.