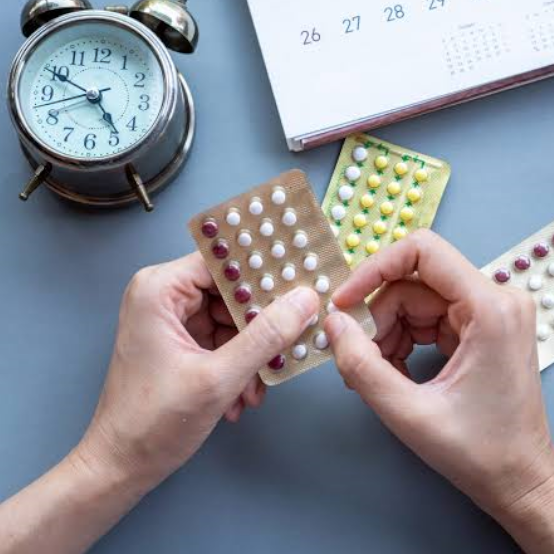
Combination birth control pills, also known as the pill, are oral contraceptives that contain estrogen and a progestin. Oral contraceptives are medicines used to prevent pregnancy. They can have other benefits too.
Combination birth control pills keep you from ovulating. This means that the pills keep your ovaries from releasing an egg. They also cause changes to the mucus in the opening of the uterus, called the cervix, and to the lining of the uterus, called the endometrium. These changes keep sperm from joining the egg.
Different types of combination birth control pills contain different doses of estrogen and progestin. Continuous-dosing or extended-cycle pills allow you to reduce the number of periods you have each year.
If you want to use combination birth control pills, your health care provider can help you decide which type is right for you.
Why it’s done
Combination birth control pills are a reliable form of contraception that’s easily reversed. Fertility can return almost right away after you stop taking the pills.
Along with preventing pregnancy, other benefits of these pills include:
-
- Lower risk of cancer of the ovaries and the lining of the uterus, ectopic pregnancy, ovarian cysts, and noncancerous breast disease
- Improvement in acne and excessive face and body hair
- Less severe menstrual cramps, called dysmenorrhea
- Reduced androgen production caused by polycystic ovary syndrome
- Decreased heavy menstrual bleeding from uterine fibroids and other causes, as well as a decrease in iron deficiency anemia related to blood loss
- Treatment of premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
- Shorter, lighter periods on an expected schedule or, for some types of combination pills, fewer periods yearly
Combination birth control pills come in different mixtures of active and inactive pills, including:
Conventional pack. One common type contains 21 active pills and seven inactive pills. Inactive pills do not contain hormones. Formulations containing 24 active pills and four inactive pills, known as a shortened pill-free interval, also are available. Some newer pills may contain only two inactive pills.
You take a pill every day and start a new pack when you finish the old one. Packs usually contain 28 days of pills. Bleeding may occur every month during the time when you take the inactive pills that are at the end of each pack.
Extended-cycle pack. These packs typically contain 84 active pills and seven inactive pills. Bleeding generally occurs only four times a year during the seven days you take the inactive pills.
Continuous-dosing pack. A 365-day pill also is available. You take this pill every day at the same time. For some people, periods stop altogether. For others, periods become significantly lighter. You do not take any inactive pills.
By decreasing or stopping periods, continuous-dosing and extended-cycle pills might have other benefits. These can include:
- Preventing and treating heavy bleeding related to uterine fibroids.
- Preventing menstrual migraines.
- Lessening the worsening effect menstruation can have on certain conditions,including seizures.
- Relieving pain related to endometriosis.
-
- Are breastfeeding
- Are older than 35 and smoke.
- Have poorly controlled high blood pressure.
- Have a history of or current blood clots, including in your legs — called deep vein thrombosis — or in your lungs — called pulmonary embolism.
- Have a history of stroke or heart disease.
- Have a history of breast cancer.
- Have migraine with aura.
- Have diabetes-related complications, such as kidney disease, eye disease or problems with nerve function.
- Have certain liver and gallbladder diseases.
- Have unexplained uterine bleeding.
- Will be confined to bed for an extended period of time after surgery or an injury or during a serious illness.